Installing additional Frameworks/en: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
Cg (Diskussion | Beiträge) |
Cg (Diskussion | Beiträge) |
||
| Zeile 171: | Zeile 171: | ||
== <div id="Cling_Installation">Cling Installation</div> (for RootCling Actions) == |
== <div id="Cling_Installation">Cling Installation</div> (for RootCling Actions) == |
||
Support for Cling is "work in progress" and currently considered an "experimental" feature. |
Support for Cling is "''work in progress''" and currently considered an "''experimental''" feature which is not available/enabled in the current deployed version. |
||
Cling (aka "Root Cling") is a |
Cling (aka "Root Cling") is a dynamic language system for C/C++. |
||
Code can be entered in C++, which is dynamically (just in time) compiled to fast machine |
Code can be entered in C++, which is dynamically (just in time) compiled to fast machine code. |
||
Cling can be downloaded from the [https://root.cern/cling Cern web site] and/or installed via a package installer: |
Cling can be downloaded from the [https://root.cern/cling Cern web site] and/or installed via a package installer: |
||
Version vom 13. März 2022, 12:14 Uhr
Inhaltsverzeichnis
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Required Frameworks Overview
- 3 Java Installation (for Groovy Actions, Web- and Mobile Testing)
- 4 .NET Installation (for the .NET bridge, Windows Apps, IronPython Actions and some Plugins 1)
- 5 Node Installation (for Node.js Actions)
- 6 Python Installation (for Python Actions)
- 7 Jython Installation
- 8 Iron Python Installation
- 9 C Compiler Toolchain Installation (for C-Actions)
- 10 Cling Installation (for RootCling Actions)
- 11 Scheme Installation (preview)
- 12 GnuPlot Installation (for Graph Attachments to the Report)
- 13 GNU Octave Installation (Matlab compatible Scripting)
- 14 TCL, Go, R and all the others
- 15 OCR (Optical Character Recognition)
Introduction[Bearbeiten]
If you intent to execute actions written for Java, Node, Python, .NET, C etc., or to test Java-, Windows- or mobile applications, additional frameworks have to be installed on your machine.
Mostly for legal reasons, but also because you will probably want to install a most up-to-date version, we do not bundle those with the expecco installation (except as noted below).
Please make sure that any required framework is installed, and they are found by expecco.
If they are already installed, but expecco fails to execute one of them, take a look at the PATH setting and/or the expecco "Execution" → "External Script Interpreters" settings. There, click on buttons labeled "?" to verify the installed version(s).
Required Frameworks Overview[Bearbeiten]
| Feature | Required Framework(s) |
|---|---|
| Java/Groovy Actions | JRE (Java Runtime Environment) or: JDK (recommended) |
| NodeJS Actions | node |
| Python Actions | Python3.x (recommended) or: Python2.x (for older Python code) |
| Iron Python Actions | .NET CLR or: Mono (on non-Windows systems) |
| Java GUI Automation | JRE (Java Runtime Environment) or: JDK (recommended) |
| Windows GUI Automation | .NET CLR |
| WebTest (Selenium Webdriver) | JRE (Java Runtime Environment) webDrivers matching your web-browser version |
| Mobile Test (Appium) | JRE (Java Runtime Environment) |
| Bridged C Actions | C compiler toolchain |
| Octave (Matlab scripts) | GNU Octave or a real Matlab |
| OCR (VNC, Screen Automation) | Tesseract language specific tessdata files |
| Vector/Canoe Plugin | .NET CLR |
Java Installation (for Groovy Actions, Web- and Mobile Testing)[Bearbeiten]
You can either install a plain Java Runtime Environment (JRE) or a full Java Development Kit (JDK). If only a JRE is installed, some functions will not work,
and we therefore recommend a JDK to be installed - typically at its standard location, "C:\Program Files\Java\jdk-xxx" (Windows), so it will run out of the box.
Expecco will try to figure out if and where Java was installed, but it it also possible to specify explicit pathes via the settings dialog.
Notice, that due to changed regulations by Oracle (i.e. legal restrictions), we may no longer provide a Java installation bundled with expecco; you should navigate to the Oracle (or OpenJDK) website and install it from there.
Also notice, that on most systems, a Java is already installed, but it may be a runtime environment only. Please verify, that a JDK is installed for the full set of features.
The expecco installation does include some required jar files (eg. groovy.jar, selenium jars and drivers etc.), but you may want to verify that they are the most up-to-date versions.
.NET Installation (for the .NET bridge, Windows Apps, IronPython Actions and some Plugins 1)[Bearbeiten]
On Windows, a .NET framework is usually already installed. On Unix/Linux systems, you can install "Mono", which may provide enough functionality for your needs. Be aware, that some functions - especially GUI browser functions - may not be present or may not work perfectly (if at all) under Mono.
Mono can be downloaded from the Mono project web site.
1) for example, the Vector/Canoe plugin requires .NET (among others).
Node Installation (for Node.js Actions)[Bearbeiten]
Goto [ https://nodejs.org/de/download/ ] and select the appropriate package for your machine. When asked if additional packages are to be downloaded, answer "yes". (Under Windows, VisualStudio build tools will then also be installed, in case any node module needs to be compiled from C/C++ code).
Open the node interpreter settings ("Extras" → "Settings" → "Execution" → "External Script Interpreters" → "Node") and verify that the "node" command is found along your PATH variable settings by clicking on the "?"-button. If found, its version should be shown.
If not found, either restart expecco (if you installed node while expecco was active), or enter the path to your node interpreter into the path field. You may even have to restart your cmd/shell session, in case the old shell environment does not contain the path to the new installed node.
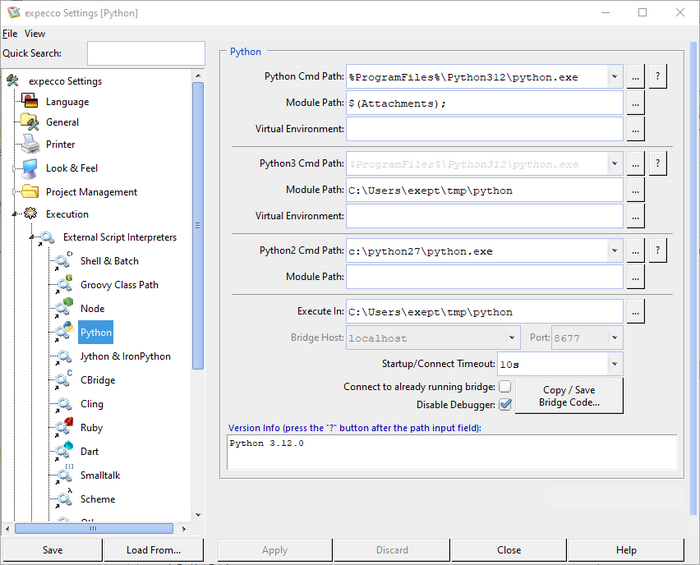
Python Installation (for Python Actions)[Bearbeiten]
Goto [ https://www.python.org/downloads/ ] and select the appropriate package for your machine. Notice, that there are both packages for python3 and python2.7 available, and you may have to install both, depending on the Python code to be executed later.
Open the Python interpreter settings ("Extras" → "Settings" → "Execution" → "External Script Interpreters" → "Python") and verify that the "python" command is found along your PATH variable settings (click on "?").
If not found, either restart expecco (if you installed Python while expecco was active), or enter the full path to your Python interpreter into the path field.
Make sure that the correct Python version is displayed (2.x vs. 3.x).
pip2 vs. pip3 vs. pip[Bearbeiten]
To install Python packages, use the "pip" command. However, this command is usually a symbolic link to either "pip2" or "pip3".
You should use "pip3" to install packages for python3, and "pip2" for python2. Thus, it is safer to use one of those or "python3 -m pip install ..." instead of "pip install ..." to ensure that the module is installed for the current version.
On some systems, no pip2 command is present by default (and installing python3 will define the "pip" command as an alias to "pip3".
To get "pip2" on those systems, execute (on the command line):
wget https://bootstrap.pypa.io/get-pip.py python2.7 get-pip.py
Things become even more confusing, if you have multiple python versions installed (for example, python3.7 and python3.9).
Then, it is best invoke pip via the python command itself.
Eg. "python3.7 -m pip install ...".
Highly Recommended Modules[Bearbeiten]
To make your life easier, install a Python debugger; either:
pip install debugpy
or
pip install ptvsd
(they are more or less interchangeable, but "ptvsd" is going to be obsoleted and being replaced by the newer "debugpy")
Without a Python debugger, breakpoints cannot be placed in bridged Python code, and you will not get a debugger on Python exceptions (you should then see a warning and hint to install "debugpy" on the Transcript and in the info area).
Jython Installation[Bearbeiten]
As a prerequisite, Java needs to be installed on your machine.
Then goto [ https://www.jython.org/download.html ], download the Jython installer and run it (choose "standard install").
If the "jython" command is not in your PATH, enter its full path in the settings dialog.
Notice that jython is a 2.x Python (at the time of writing).
Iron Python Installation[Bearbeiten]
As a prerequisite, you'll need a .NET CLR (common language runtime) or mono (on Unix systems). On Windows systems, a reasonable CLR Version is usually already installed. Then go to [ https://ironpython.net/download ] or [ https://github.com/IronLanguages/ironpython3 ] and follow the instructions.
After the download, IronPython is typically installed in "C:\Program Files\IronPython 3.x", and you should enter the path "C:\Program Files\IronPython x.y\ipy.exe" into the IronPython command path field in the python settings dialog (or simply "ipy", if it is in your PATH).
Notice that previous IronPython versions were 2.x Pythons, which will sooner or later become autdated. It is therefore recommended to download or upgrade to a 3.x version (if your code is 3.x compatible).
C Compiler Toolchain Installation (for C-Actions)[Bearbeiten]
C Compiler Toolchain Installation[Bearbeiten]
You need a C-compiler toolchain to be installed for C-coded actions.
- On Unix/Linux systems, these are usually already present on the machine (try "
cc --version" in a shell window; if you get a reasonable response, you are usually ready to go). - On Windows, install one of "Borland", "VisualC", "VisualC Redistributable" or "MingGW".
We recommend MingGW. - On OSX, you have to install "XCode" or the "Command Line Tools" subset.
Windows + Borland (32bit)[Bearbeiten]
- get the free Borland command line tools (see https://borland-c.software.informer.com/5.5) and install them (typically, under "C:\borland\bcc55")
- ensure that the link.cfg and bcc55.cfg files are present in the "C:\borland\bcc55\bin" directory.
- verify the installation by typing "bcc32". A help message should appear.
Windows + Visual-C[Bearbeiten]
*** to be documented ***
Windows + Mingw64[Bearbeiten]
- get the mingw64 compiler and install it.
- verify the installation by typing "gcc --help".
When a C-coded action is about to be executed, its C-code will be compiled just in time using that toolchain. For that, the cBridge executes a configurable batch or shell script.
For some commonly used toolchains, corresponding scripts are provided, but you can or may have to add your own script(s), in case you need special compile options, additional link library options or if you want to compile with a compiler not supported by the standard installation (eg. Intel compilers).
If you get compilation errors, take a look at the "compile_xxx" scripts in "packages/exept/expecco/bridgeFramework/cBridge/cLibrary" under the expecco installation folder.
If required, add your own script to call whatever compiler you need, and select it in the cBridge settings dialog ("Extras" → "Settings" → "Execution" → "External Language Interpreters" → "CBridge").
Notice, that we currently do not provide compilation scripts for C++; however, by declaring entry-functions (extern "C") in your C++ code, these can be called from C.
If no toolchain is installed, you can still see and edit C-code actions, but obviously no execute them.
C Compiler Toolchain at Test-Execution Time[Bearbeiten]
You can tell expecco to embed a pre-compiled object file into the saved ".ets" suite file ("Store Object Files" checkbox in the settings dialog). If checked, C-Bridge actions will be compiled by your current session (using the configured toolchain) and the generated object files will be saved with the suite. When the suite is later executed, no compiler toolchain will be needed on the test machine.
Expecco does not include cross compilation support; that means, that only object files for the current architecture can be generated. However, if you load the suite into another architecture's expecco, additional object files for that other architecture will be generated and added to the ".ets" when saved. So afterwards, object files for both architectures will be present in the ets.
To summarize, if you want to deploy a library with embedded C-actions, which will have to be executed on (say) both a Linux and a Windows machine, where both test-execution machines have no compiler toolchain installed, perform the following steps:
- load the suite on a Linux machine (with C-compiler toolchain available)
- ensure that the "Store Object Files" flag is checked.
- Save the suite
- load the saved ".ets" on a Windows machine (with C-toolchain available)
- Save it again.
The last saved ".ets" will now contain object files for both architectures. Be aware, that you may have to repeat the steps for 32 and 64 bit architectures, if the suite is to be executed eventually on both.
Cling Installation (for RootCling Actions)[Bearbeiten]
Support for Cling is "work in progress" and currently considered an "experimental" feature which is not available/enabled in the current deployed version.
Cling (aka "Root Cling") is a dynamic language system for C/C++. Code can be entered in C++, which is dynamically (just in time) compiled to fast machine code.
Cling can be downloaded from the Cern web site and/or installed via a package installer:
- Linux
- -- see https://root.cern/download/cling/ --
- Windows
- Sorry, to our knowledge, there exists no ready-to-install version for Windows at the time of writing this document.
- OS X(Mac)
brew install cling
Depending on whether cling is found along your path, or you want to select a particular version,
specify the cling installation folder in the cling settings dialog "Extras" → "Settings" → "Execution" → "External Language Interpreters" → "Cling".
There, click on the "?" button to verify that cling is found.
Scheme Installation (preview)[Bearbeiten]
Support for Scheme is "work in progress", currently disabled and is planned for a 22.x version. You can configure expecco to either use any standard scheme interpreter (whichever is installed as "scheme"command), or to use an explicit implementation. Currently, supported are ChezScheme and ChickenScheme.
Chicken Scheme[Bearbeiten]
Chicken can be compiled from source or installed via a package manager.
- Windows
- https://chocolatey.org/packages/chicken/
- or:
- see https://wiki.call-cc.org/platforms#microsoft-windows-
- Linux
- see https://wiki.call-cc.org/platforms#linux
- OS X (mac)
- brew install chicken
- or:
- see https://wiki.call-cc.org/platforms#mac-os-x
Chez Scheme[Bearbeiten]
See [ https://github.com/cisco/ChezScheme ] for instructions.
A Windows binary and sources of release 9.5.4 are found at [ https://github.com/cisco/ChezScheme/releases/tag/v9.5.4 ].
GnuPlot Installation (for Graph Attachments to the Report)[Bearbeiten]
Gnuplot makes it easy to add graphs for measurement data or statistics to the report and/or to create attachments for them. To install gnuplot execute (in a terminal):
- Linux
- -- to be determined and documented --
- please refer to the official Gnuplot website: http://www.gnuplot.info/download.html
- Windows
- -- to be determined and documented --
- please refer to the official Gnuplot website: http://www.gnuplot.info/download.html
- OS X (Mac)
brew install gnuplot- or download a binary package eg. from:
- https://csml-wiki.northwestern.edu/index.php/Binary_versions_of_Gnuplot_for_OS_X
GNU Octave Installation (Matlab compatible Scripting)[Bearbeiten]
- OS X (Mac)
- Download a dmg from
- https://wiki.octave.org/Octave_for_macOS
- or:
- https://octave-app.org
- or:
sudo port install octave
- Windows
- Download from https://www.gnu.org/software/octave/download.
Warning: octave is huge (roughly 1Gb download).
Also notice: octave needs gnuplot to generate image files from graphs.
If you are already using Matlab, set the path to the matlab executable in the "Execution" → "External Script Interpreter" settings.
TCL, Go, R and all the others[Bearbeiten]
If you use those, you probably know how to install and update them. Follow the usual installation instructions and - unless the interpreter is found along your PATH setting, define the path in the expecco "Execution" → "External Script Interpreters" settings dialog.
OCR (Optical Character Recognition)[Bearbeiten]
In order to extract text from a bitmap image, an OCR framework is needed.
Both open source and commercial frameworks can be found and used. Good results are achieved by the free (and open source) "Tesseract" framework, which we recommended, unless you already have a more powerful non-free commercial OCR framework at hand (although supported, we do NOT recommend capture2Text or GNU-ocrad, as they do not provide detailed per-word information or deliver poor recognition results at the time of writing this document).
Tesseract is hosted at [ https://github.com/tesseract-ocr/tessdoc ] and can be downloaded from [ https://github.com/tesseract-ocr/tessdoc/blob/master/Downloads.md ].
Follow the installation instructions there.
- Windows and OS X
- binaries are found at [ https://github.com/UB-Mannheim/tesseract/wiki ]
In order to recognize national language characters (eg. accents, diareses/Umlauts), you'll also need language specific Tesseract-Data files. Please also install those for German, French, etc. from [ https://github.com/tesseract-ocr/tessdata ].