Tools ModelTranslationEditor/en: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
Cg (Diskussion | Beiträge) |
Cg (Diskussion | Beiträge) |
||
| (35 dazwischenliegende Versionen desselben Benutzers werden nicht angezeigt) | |||
| Zeile 1: | Zeile 1: | ||
== Backround Information == |
|||
Expecco uses two separate national language translation schemes: |
Expecco uses two separate national language translation schemes: |
||
# language translations for the GUI (i.e. menus, button labels, window titles etc. |
# language translations for the GUI (i.e. menus, button labels, window titles etc.). The so called "''UI language''". |
||
# language translations for model elements (blocks, steps, pins, etc.) and especially text presented to the user by Dialog actions |
# language translations for model elements (blocks, steps, pins, etc.) and '''especially''' text presented to the user by Dialog actions or user defined UIs. The so called "''Model language''". |
||
Both languages can be changed independently in the settings dialog ("''Extras''" → "''Settings''" → "''Language''"). |
Both languages can be changed independently in the settings dialog ("''Extras''" → "''Settings''" → "''Language''"). |
||
<br>However, the translation information is stored in separate places |
<br>However, the translation information is stored in separate places: |
||
* The translation strings for the |
* The translation strings for the UI language are bundled with the original distribution provided by eXept, and more or less fix (although, a knowledgeable user can easily add new languages and/or modify existing language translations, as these files are plain regular text files in the "<code>resources</code>" subfolders). |
||
* The model language translations are stored in the project-file itself, and are attached to the top-level "Project" tree item. These are stored in and transported with the testSuite-file. |
* The model language translations are stored in the project-file itself, and are attached to the top-level "Project" tree item. These are stored in and are transported with the testSuite-file. |
||
Defining national translations for model elements is very useful in multi-language companies. |
Defining national translations for model elements is very useful in multi-language companies. |
||
| Zeile 15: | Zeile 16: | ||
Even more important are texts and labels shown in GUI dialogs (confirmations, warn boxes or reports) both in the common dialogs from the Standard Library, and texts in custom dialogs (i.e. in actions with GUI or manual test steps). Those are also translated via the "''Model Language Translation''" mechanism. |
Even more important are texts and labels shown in GUI dialogs (confirmations, warn boxes or reports) both in the common dialogs from the Standard Library, and texts in custom dialogs (i.e. in actions with GUI or manual test steps). Those are also translated via the "''Model Language Translation''" mechanism. |
||
Model language translations are added, modified and possibly removed using the "''Model Translation Editor''", which is opened via the "''Extras''" → "'' |
Model language translations are added, modified and possibly removed using the "''[[#Modellanguage Translation Editor|Model Translation Editor]]''", which is opened via the "''Extras''" → "''Translation (Model Language)''" menu item. |
||
For development in a multi-language environment, it is a good strategy to choose one language as the primary language, and base all translations on that. Usually this would be English. However, this is not a strict requirement: any language can be added later at any time and in any order. Thus, it is also possible to start in German, and add French, Italian and English translations later. |
For development in a multi-language environment, it is a good strategy to choose one language as the primary language, and base all translations on that. Usually this would be English. However, this is not a strict requirement: any language can be added later at any time and in any order. Thus, it is also possible to start in German, and add French, Italian and English translations later. |
||
==== Language and Territory (Dialect) ==== |
|||
Language identifiers are specified in "[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_ISO_639_language_codes ISO-639]" and "[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/IETF_language_tag IETF language tag]" and consist of two 2-character parts separated by a hyphen or underline. The first part is the language, the second the territory or dialect or variant. |
|||
<br>Some typical examples are: |
|||
de-DE ... German |
|||
de-AT ... Austrian German |
|||
en-GB ... British English |
|||
en-US ... US English |
|||
fr-FR ... French |
|||
it-IT ... Italian |
|||
es-ES ... Spanish |
|||
pt-PT ... Portuguese |
|||
pt-BR ... Brasilian Portuguese |
|||
== Action, Step and Pin Names == |
== Action, Step and Pin Names == |
||
For the following example, we assume, that the tree elements are initially named in English, |
For the following example, we assume, that the tree elements are initially named in English (the ''original language''), |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
Perform the following steps: |
Perform the following steps: |
||
# open the "Model Language Editor", |
# open the "Model Language Editor", |
||
# Fetch all existing tree-element names via the "''Utilities''" & |
# Fetch all existing tree-element names via the "''Utilities''" → "''Fetch Names from Tree''" menu item) |
||
# specify the language to be |
# specify the original language to be english (via "''Utilities''" → "''Set Original Language''" menu item) |
||
# specify the target language to be added (i.e. select "de_de") |
|||
# add the translation, by selecting an untranslated name and editing its "translated" value |
# add the translation, by selecting an untranslated name and editing its "translated" value |
||
# change the language to "fr_fr" and repeat the previous step |
# change the target language to "fr_fr" and repeat the previous step |
||
# confirm by saving via the "''Save''" menu item. |
# confirm by saving via the "''Save''" menu item. |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
To see the effect, in your tree/diagrams, change the model language in the settings dialog.<br>Notice, that the GUI's language remains the same; English, in this example. |
To see the effect, in your tree/diagrams, change the model language in the settings dialog.<br>Notice, that the GUI's language remains the same; English, in this example. |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
Hint: as the length of word differs by some 20-30% among languages, some steps may now be too small to show the possibly longer names. |
Hint: as the length of word differs by some 20-30% among languages, some steps may now be too small to show the possibly longer names. |
||
Therefore, it is a good idea, to reserve some additional space for every new step by making them somewhat wider right from the start. |
Therefore, it is a good idea, to reserve some additional space for every new step by making them somewhat wider right from the start. |
||
== Dialog Messages / Report Strings == |
== Dialog Messages / Report Strings / Pin Input Strings == |
||
For a step's input string to be translated, select the pin and open its pin menu |
For a step's input string to be translated, select the pin and open its pin menu with a right click. |
||
Find the submenu under "Attributes" and turn on the checkbox for "Model Language Translated". |
Find the submenu under "''Attributes''" and turn on the checkbox for "''Model Language Translated''". |
||
Then, any incoming string will be translated via the mechanism (or left untranslated if no translation was defined for it). |
Then, any incoming string will be translated via the mechanism (or left untranslated if no translation was defined for it). |
||
== Explicit Translation in Elementary Code == |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
The translation framework's API can also be used from elementary actions or via actions from the "NLS_Support_Library" (new in vsn25.1). |
|||
==== API Functions ==== |
|||
* Expecco::ExpeccoPreferences current expeccoModelLanguageAndTerritory |
|||
:: provides the current model language (eg. 'en_gb', 'en_us', 'de_de', 'fr_fr' etc.). |
|||
* ''map'' := self topProject modelLanguageResourcesForLanguage:''aLanguage'' |
|||
:: a string mapping dictionary, containing translations for a language |
|||
* ''aMap'' string:''someString'' |
|||
:: does a translation; if no translation is present, ''someString'' is returned |
|||
* ''aMap'' string:''someString'' with:''arg'' |
|||
:: does a translation, replacing "%1" by ''arg's'' printstring |
|||
* ''aMap'' string:''someString'' with:''arg1'' ... with:''argN'' |
|||
:: ditto, up to 7 arguments |
|||
* ''aMap'' string:''someString'' withArguments:''argArrayOrDictionary'' |
|||
:: ditto, any number of arguments; either sliced in by number ("%1", "%2", ...) when arg must be an Array, or by name ("%(name1)", "%(name2)", ...) when arg must be a dictionary |
|||
* ''aMap'' string:''someString'' default:''defaultString'' |
|||
:: does a translation; if no translation is present, ''defaultString'' is returned |
|||
* ''aMap'' string:''someString'' default:''defaultString'' withArguments:''argArrayOrDictionary'' |
|||
:: ditto, any number of arguments |
|||
== Tools == |
|||
==== Modellanguage Translation Editor ==== |
|||
The editor is opened via "''Extras''" → "''Translation (Model Language)''": |
|||
[[Datei:ModelLanguageEditor1.png|400px]] |
|||
To fetch strings used by the project, select one of items from the "''Utilities''" menu. |
|||
To translate using external tools or translation services, export the mappings as CSV an reimport the filled table via the "''File''" menu. |
|||
== Tips & Tricks == |
|||
==== Font ==== |
|||
If CJK (Chinese/Japanes/Korean) characters are in the translation, |
|||
you should select a font which actually contains glyphs for those characters. |
|||
There are several free Unicode fonts available for download. For example, GNU FreeFont is a free family of scalable outline fonts that are Unicode-encoded. |
|||
Additionally, there are projects like the Free UCS Outline Fonts, which aim to support as many Unicode characters as possible. |
|||
Another option is the DejaVu project, which provides a free sans-serif Unicode font. |
|||
You can also find a selection of free Unicode fonts on websites such as FontSpace and 1001 Fonts. |
|||
For more specialized needs, there are fonts like Noto, designed by Google to cover all the scripts encoded in the Unicode standard. |
|||
==== Case Sensitivity ==== |
|||
If no translation is found for an original string and the original starts with a letter, expecco looks for a translation for the opposite case. If found, the translation with changed case is used. Sorry, but that work for the first character only. |
|||
==== Prefixes and Suffices with Special Characters ==== |
|||
If no translation is found for an original string and the original starts or ends with a special character (eg. ".,;()[]'etc.), then expecco looks for a translation without those special characters. If that is found, the translation of that with added prefix and suffix are used. |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
Be aware, that different languages will use different sentence building rules; so subject or object are often in different position within a sentence. For example, the english |
Be aware, that different languages will use different sentence building rules; so subject or object are often in different position within a sentence. For example, the english |
||
| Zeile 67: | Zeile 136: | ||
To fix this, use %-placeholders and format the resulting string. Instead of the above, define a translation like: |
To fix this, use %-placeholders and format the resulting string. Instead of the above, define a translation like: |
||
"Do you really want to delete the file %1?" -> "Wollen Sie die Datei %1 wirklich löschen?" |
"Do you really want to delete the file %1?" -> "Wollen Sie die Datei %1 wirklich löschen?" |
||
and then provide the actual filename |
and then provide the actual filename either in elementary code: |
||
resources string:'Do you really want to delete the file %1?' with:fileName |
resources string:'Do you really want to delete the file %1?' with:fileName |
||
or |
or |
||
i'Do you really want to delete the file {fileName}?' |
i'Do you really want to delete the file {fileName}?' |
||
Or in a compound action, use the "String [format]" action and pass the string (with placeholders) to its first input, and the args to be sliced in to the [1]..[n] |
Or in a compound action, use the "String [format]" action and pass the string (with placeholders) to its first input, and the args to be sliced in to the [1]..[n] inputs. |
||
Don't forget to |
Don't forget to turn on the pin's "''Model Translate''" attribute. |
||
---- |
---- |
||
Aktuelle Version vom 16. Juli 2025, 14:26 Uhr
Inhaltsverzeichnis
Backround Information[Bearbeiten]
Expecco uses two separate national language translation schemes:
- language translations for the GUI (i.e. menus, button labels, window titles etc.). The so called "UI language".
- language translations for model elements (blocks, steps, pins, etc.) and especially text presented to the user by Dialog actions or user defined UIs. The so called "Model language".
Both languages can be changed independently in the settings dialog ("Extras" → "Settings" → "Language").
However, the translation information is stored in separate places:
- The translation strings for the UI language are bundled with the original distribution provided by eXept, and more or less fix (although, a knowledgeable user can easily add new languages and/or modify existing language translations, as these files are plain regular text files in the "
resources" subfolders).
- The model language translations are stored in the project-file itself, and are attached to the top-level "Project" tree item. These are stored in and are transported with the testSuite-file.
Defining national translations for model elements is very useful in multi-language companies. Especially, when considering the documentation aspect of the graphical programming model: every programmer can see the action, step and pin names in his/her native language.
Even more important are texts and labels shown in GUI dialogs (confirmations, warn boxes or reports) both in the common dialogs from the Standard Library, and texts in custom dialogs (i.e. in actions with GUI or manual test steps). Those are also translated via the "Model Language Translation" mechanism.
Model language translations are added, modified and possibly removed using the "Model Translation Editor", which is opened via the "Extras" → "Translation (Model Language)" menu item.
For development in a multi-language environment, it is a good strategy to choose one language as the primary language, and base all translations on that. Usually this would be English. However, this is not a strict requirement: any language can be added later at any time and in any order. Thus, it is also possible to start in German, and add French, Italian and English translations later.
Language and Territory (Dialect)[Bearbeiten]
Language identifiers are specified in "ISO-639" and "IETF language tag" and consist of two 2-character parts separated by a hyphen or underline. The first part is the language, the second the territory or dialect or variant.
Some typical examples are:
de-DE ... German de-AT ... Austrian German en-GB ... British English en-US ... US English fr-FR ... French it-IT ... Italian es-ES ... Spanish pt-PT ... Portuguese pt-BR ... Brasilian Portuguese
Action, Step and Pin Names[Bearbeiten]
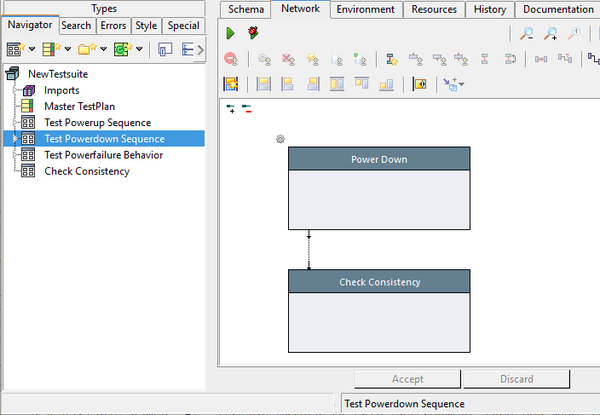
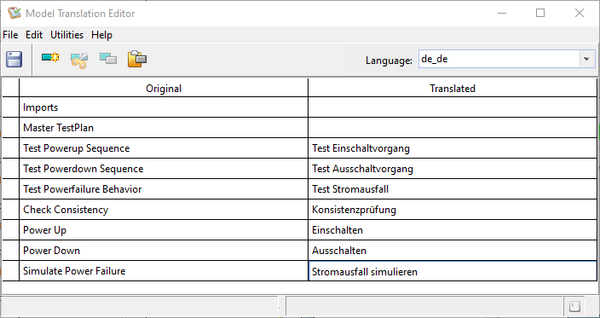
For the following example, we assume, that the tree elements are initially named in English (the original language),
and translations are to be added for German and French (target languages).
Perform the following steps:
- open the "Model Language Editor",
- Fetch all existing tree-element names via the "Utilities" → "Fetch Names from Tree" menu item)
- specify the original language to be english (via "Utilities" → "Set Original Language" menu item)
- specify the target language to be added (i.e. select "de_de")
- add the translation, by selecting an untranslated name and editing its "translated" value
- change the target language to "fr_fr" and repeat the previous step
- confirm by saving via the "Save" menu item.
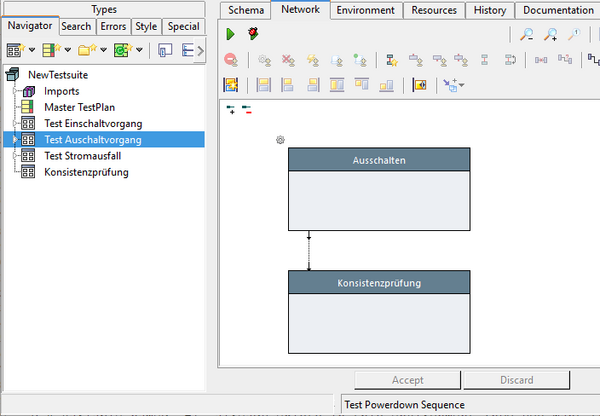
To see the effect, in your tree/diagrams, change the model language in the settings dialog.
Notice, that the GUI's language remains the same; English, in this example.
Hint: as the length of word differs by some 20-30% among languages, some steps may now be too small to show the possibly longer names. Therefore, it is a good idea, to reserve some additional space for every new step by making them somewhat wider right from the start.
Dialog Messages / Report Strings / Pin Input Strings[Bearbeiten]
For a step's input string to be translated, select the pin and open its pin menu with a right click. Find the submenu under "Attributes" and turn on the checkbox for "Model Language Translated". Then, any incoming string will be translated via the mechanism (or left untranslated if no translation was defined for it).
Explicit Translation in Elementary Code[Bearbeiten]
The translation framework's API can also be used from elementary actions or via actions from the "NLS_Support_Library" (new in vsn25.1).
API Functions[Bearbeiten]
- Expecco::ExpeccoPreferences current expeccoModelLanguageAndTerritory
- provides the current model language (eg. 'en_gb', 'en_us', 'de_de', 'fr_fr' etc.).
- map := self topProject modelLanguageResourcesForLanguage:aLanguage
- a string mapping dictionary, containing translations for a language
- aMap string:someString
- does a translation; if no translation is present, someString is returned
- aMap string:someString with:arg
- does a translation, replacing "%1" by arg's printstring
- aMap string:someString with:arg1 ... with:argN
- ditto, up to 7 arguments
- aMap string:someString withArguments:argArrayOrDictionary
- ditto, any number of arguments; either sliced in by number ("%1", "%2", ...) when arg must be an Array, or by name ("%(name1)", "%(name2)", ...) when arg must be a dictionary
- aMap string:someString default:defaultString
- does a translation; if no translation is present, defaultString is returned
- aMap string:someString default:defaultString withArguments:argArrayOrDictionary
- ditto, any number of arguments
Tools[Bearbeiten]
Modellanguage Translation Editor[Bearbeiten]
The editor is opened via "Extras" → "Translation (Model Language)":
To fetch strings used by the project, select one of items from the "Utilities" menu.
To translate using external tools or translation services, export the mappings as CSV an reimport the filled table via the "File" menu.
Tips & Tricks[Bearbeiten]
Font[Bearbeiten]
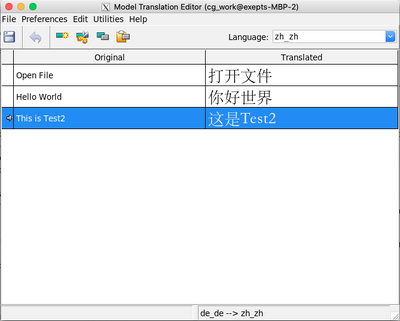
If CJK (Chinese/Japanes/Korean) characters are in the translation, you should select a font which actually contains glyphs for those characters.
There are several free Unicode fonts available for download. For example, GNU FreeFont is a free family of scalable outline fonts that are Unicode-encoded. Additionally, there are projects like the Free UCS Outline Fonts, which aim to support as many Unicode characters as possible. Another option is the DejaVu project, which provides a free sans-serif Unicode font. You can also find a selection of free Unicode fonts on websites such as FontSpace and 1001 Fonts. For more specialized needs, there are fonts like Noto, designed by Google to cover all the scripts encoded in the Unicode standard.
Case Sensitivity[Bearbeiten]
If no translation is found for an original string and the original starts with a letter, expecco looks for a translation for the opposite case. If found, the translation with changed case is used. Sorry, but that work for the first character only.
Prefixes and Suffices with Special Characters[Bearbeiten]
If no translation is found for an original string and the original starts or ends with a special character (eg. ".,;()[]'etc.), then expecco looks for a translation without those special characters. If that is found, the translation of that with added prefix and suffix are used.
Slicing Words into a Translation[Bearbeiten]
Be aware, that different languages will use different sentence building rules; so subject or object are often in different position within a sentence. For example, the english
"Do you really want to delete the file XXX?"
would be in German:
"Wollen Sie die Datei XXX wirklich löschen?"
That means that a simple string concatenation is usually not giving you good translations. In the previous example, the German translation "Wollen Sie die Datei wirklich löschen XXX" sounds horrible to every german.
To fix this, use %-placeholders and format the resulting string. Instead of the above, define a translation like:
"Do you really want to delete the file %1?" -> "Wollen Sie die Datei %1 wirklich löschen?"
and then provide the actual filename either in elementary code:
resources string:'Do you really want to delete the file %1?' with:fileName
or
i'Do you really want to delete the file {fileName}?'
Or in a compound action, use the "String [format]" action and pass the string (with placeholders) to its first input, and the args to be sliced in to the [1]..[n] inputs. Don't forget to turn on the pin's "Model Translate" attribute.
Back to Online Documentation.